Git fundamentals
Theory: Stash
Imagine this: you're working on an important task and have changed quite a few files. At this point, an urgent task arises to make a change in the source code that's unrelated to what you're currently working on. Your changes are not ready yet and should not go into the repository. What to do?
In the simplest case, if your changes don't overlap with the changes you made during the urgent task, you can make the necessary corrections, add them to the index, commit them, and run them. But this is usually inconvenient and not always possible. What if you need to make changes in the files you're working with right now?
This situation occurs regularly with experienced developers and, fortunately, it is easily resolved. Git has a set of commands that allow you to "hide" changes in the working directory and restore them when needed. Let's give it a try:
git stash does not delete files, they go to a special place inside the .git directory to «be saved». This command does not touch the new files as they are not yet part of the repository.
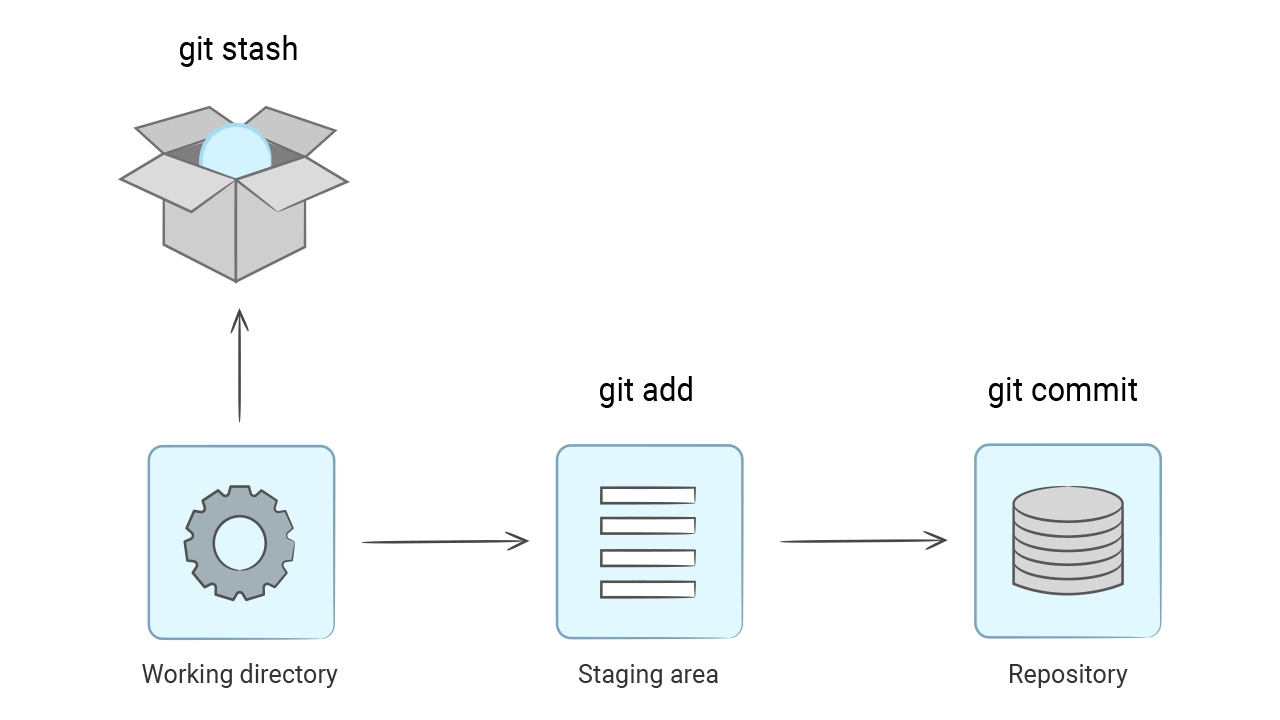
After you have made all the necessary changes on a clean working directory, you can revert the hidden changes with the git stash pop command:
The files came back since they were in the stash.
Stash in git works like a stack. It allows you to save any number of changes inside and restore them in reverse order: