Python Basics
Theory: Logical operators
We already know how to write functions that check individual conditions. We will learn how to build compound conditions n this lesson.
Suppose a site needs a password to be longer than eight characters and shorter than twenty characters when registering. You see 8 < x < 20 in mathematics, but you cannot do that in many programming languages.
Let us try to write two separate logical expressions and connect them with the operator AND:
The password is longer than 8 characters AND the password is shorter than 20 characters
Here is a function that takes the password and tells you whether it matches the conditions (True or False):
In mathematics, this is called a conjunction. It has operands — compound expressions.
The whole expression is true if each operand is true. In other words, AND means both.
The priority of this operator is lower than that of comparison operators. So, the expression length > 8 AND length < 20 works correctly without parentheses.
In addition to AND, we also have OR. It is a disjunction, meaning one or the other or both. The a or b expression is true if one or both operands are true. Otherwise, it is false.
We can combine operators in any number and any order. You can use parentheses to specify the priority when and and or occur in the code.
Here is an example of an advanced function that determines if a password is correct:
Suppose we want to buy an apartment that meets these conditions: at least 100 square meters on any street OR at least 80 square meters but on Main Street.
We will write a function to check an apartment. It takes two arguments:
- The area as a number
- The street name as a string
Here is the code:
The area of mathematics that deals with logical operators is Boolean algebra.
Below, you will see truth tables. You can use them to determine what result you get if you apply the operator.
The AND operator
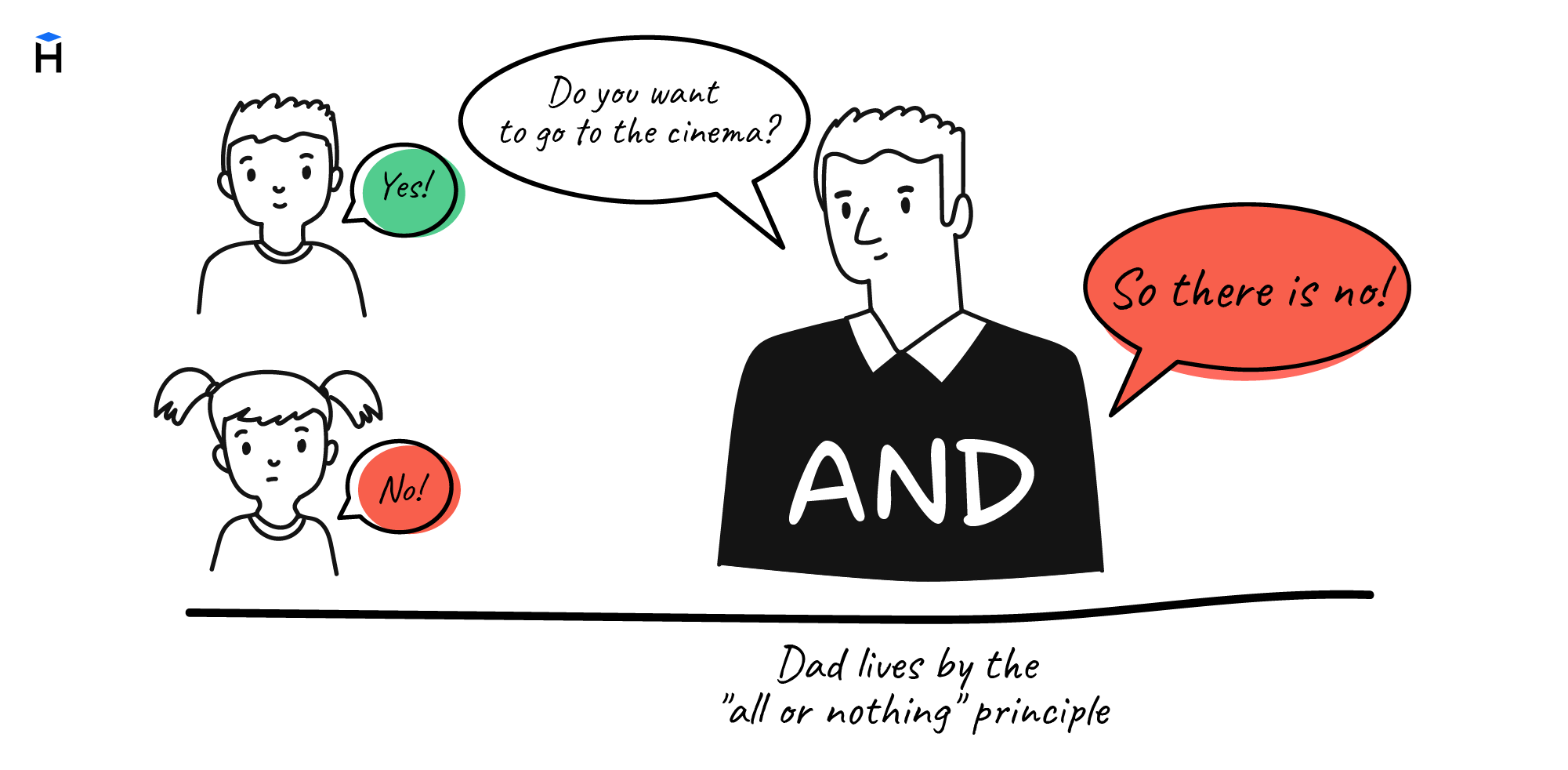
Here is the truth table:
The OR operator
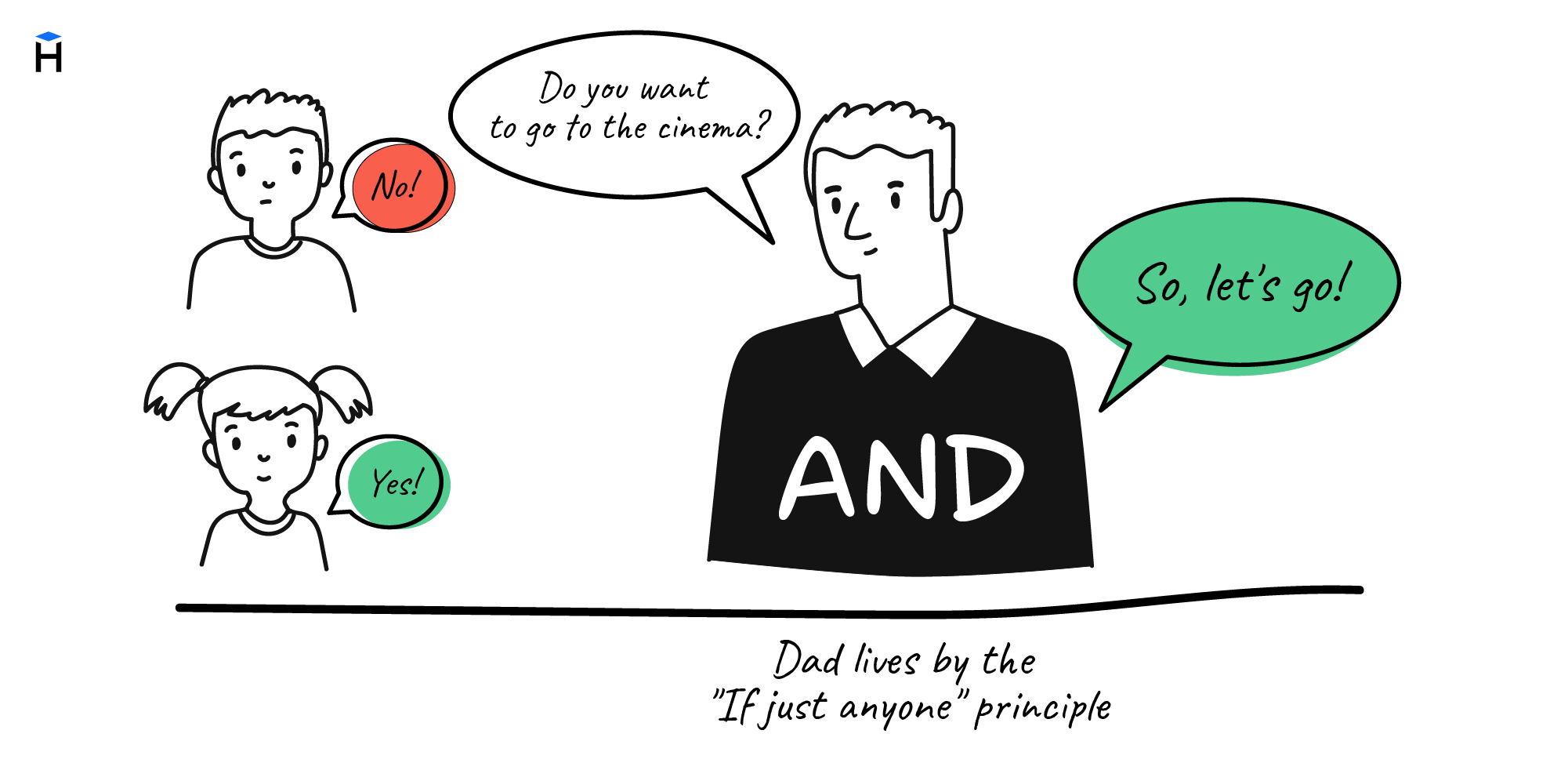
Here is the truth table:
The negation
Along with the logical operators AND and OR, there is also an operation called negation. It changes the logical meaning to the opposite. In programming, negation corresponds to the unary operator not:
For example, if there is a function that checks if a number is even, then you can use negation to check if a number is odd:
In the example above, we added not to the left of the function call and got the opposite action.
Negation is a tool with which you can express intended rules in code without writing new functions.
If you write not not is_even(10), the code will still work:
In logic, double negation means positive:
Now you know how to work with AND, OR, and NOT operators. They allow you to specify compound conditions with two or more logical expressions.